Copper stands as one of the most preferred metals for electrical conductivity, despite having several drawbacks. To mitigate these shortcomings, copper is often tin-coated, enhancing its suitability for various applications.
Wires and cables come in a variety of sizes, styles, and applications, making it crucial for users to consider longevity as a key factor. Service life is indeed a fundamental determinant in selecting the appropriate wire for any project. This has led to the development of tinned copper from pure copper material.

Reasons for Tinning Copper
Pure copper, while an excellent conductor of electricity, experiences reduced functionality when corroded, particularly in highly humid or wet environments. In such conditions, pure copper corrodes and weakens rapidly, necessitating the solution of tinning.
Tinning not only enhances copper’s strength, enabling it to function effectively in all circumstances, but also boosts its performance capabilities. Additionally, tinning provides resistance and safety against high temperatures and humidity levels.
The tinning process, which cannot be done manually, is achieved through an electrical chemical process known as electroplating.
Experts note that the demand for tinned copper cables is increasing daily, expanding their applications in industrial appliances and equipment. Globally, more electrical-based businesses are purchasing this product in bulk to meet the growing supply and demand.
Understanding Tin Copper wire and Bare Copper wire
Tinned and pure copper wire has different expressions in dynamic ways based on their applications. Tinned Copper Cable is copper plated with a base alloy that is mostly tin that enhances the natural abilities of copper to make it more robust in Performance and suitable for
Bare copper wire refers to a copper wire that’s simply derived from a pure copper rod. It has no insulating layer, and its material is unique, soft, and an excellent electrical conductor. Electricians normally make use of pure copper wire in visible ground wires and in simple electrical connections.
Difference between tinned copper versus Bare Copper
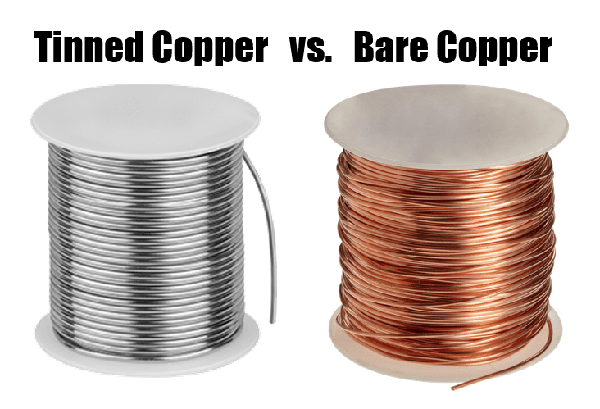
The primary distinction between these two materials lies in their appearance. Tin-plated copper wire exhibits a silvery hue, mirroring the color of tin metal, whereas pure copper wire appears as a golden-yellow, derived from the pure copper rod.
Moreover, their performance differs significantly. Tin-plated copper cable demonstrates superior electrical conductivity compared to its competitor materials. Additionally, it boasts enhanced corrosion and oxidation resistance, thereby prolonging its performance life and longevity. Tin-plated copper wires are also easier to fold, stretch, and expand during installation than pure copper wires.
Furthermore, the production process of tin-plated copper cables is more intricate than that of pure copper wire. The application of the hot tin plating process to the pure copper wire results in a surface coated with a thin layer of tin.
The tinning process is complex and demands sufficient time to achieve success. Consequently, tin-plated copper wire is more expensive than pure copper wire.
Advantages of Tinned copper versus Bare copper
Although both tinned copper and pure copper wires provide comparable results in terms of electrical connectivity, tinned copper wires offer superior resistance to humidity, chemicals, acids, and corrosion. Pure copper wire is less resilient in wet or saltwater environments compared to tin copper cables, which can endure harsh environmental conditions.
Tin-plated copper wire boasts an extended cable life and ease of soldering. Conversely, while pure copper wire may also exhibit good solderability, its service life is contingent upon the application conditions. Additionally, both types of wires can be used with cable gauges ranging from 12 to 18 AWG and operate efficiently within an optimal temperature range of 40 degrees Celsius to 105 degrees Celsius.
However, added advantages of pure copper include:
- High thermal conductivity.
- High melting point.
- High strength.
- It is highly resistant hence preventing damage caused while handling a large amount of electricity.
Application of Tinned Copper Cables versus Pure Copper Wire
The application of tin-plated copper wire is determined by the environment. It is suitable for use in equipment found in water and sewage treatment facilities, as well as projects exposed to excessive oil, gas, or water. Utility projects often utilize tin-plated copper cable, and electricians can install it in environments with high salt concentrations.
Tin-plated copper extends the service life of the cable, so planning for its use in highly corrosive areas can prevent and reduce the need for wire replacements in the future. Additionally, tin-plated copper wire is also applicable in wiring installation processes within the marine industry and major electronic appliances.
However, copper wire can also be used in electrical transmission, grounding systems, hookups, jumpers, and other electrical appliances.
Conclusion
While tinned copper cable and bare copper wire may exhibit similar or equivalent conductivity, they vary greatly in their application and performance dynamics. The tinning process enhances tinned copper’s resistance to corrosion and oxidation, thereby prolonging its lifespan and service duration. However, it is crucial to make an informed choice when purchasing either type of copper wire to avoid acquiring counterfeit products.
Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.