
The pitch of a connector refers to the spacing between the centers of two pins within the same connector. One might inquire about the significance of this pitch. Indeed, the pitch is crucial and must be taken into account during circuit design by the manufacturer. The importance of considering the pitch when purchasing a connector varies based on its application.
Ignoring this aspect can lead to additional costs due to purchasing the wrong type of connector. This often occurs when the connector’s pitch is incompatible with its mating part, preventing proper fitment. Furthermore, the confusion between different standards and nomenclature can impair the connector’s functionality.
Pitches of Connectors in Metrics and Standards Units
The most common pitches are;
- 1inches equivalent to 2.54 mm, which is standard for breadboards.
A connector with a 2.54mm pitch is specifically engineered for environments subject to high vibration. It is compatible with slightly taller headers that are fully shrouded. Additionally, it can be utilized in conjunction with high-pressure housings and applications requiring TPA enhancement. You will observe that a 2.54mm pitch connector boasts greater strength and ruggedness compared to connectors featuring lower pitch values. Nevertheless, it maintains its properties when employed for low-profile applications, such as power transmission and signaling.
- 05 inches which are equivalent to 1.27mm
Other pitches include;
- The 1.20mm pitch
- The 1.25mm pitch
- The 1.50mm pitch
- The 6mm pitch
- The 10mm pitch
- The 0.3in pitch
- The 0.4in pitch
However, it is crucial to keep in mind the pitch of a connector and its compatibility when purchasing or replacing a connector, header, motherboard, daughterboard, and any accessories that incorporate these components.
Measuring Connector Pitch
When intending to attach a ribbon cable to a board’s header on a microcontroller unit, it is imperative that the ribbon cable meets the required specifications. Additionally, it is necessary to be knowledgeable about the optimal method for fitting the connector. Firstly, you must ask yourself: what is the connector’s pitch? Therefore, identify the distance between the connector’s pins. Always check the pitch of the connector on the datasheet, as it can be difficult to determine the pitch manually without it. This is because the distance from one pin to another is often too small.
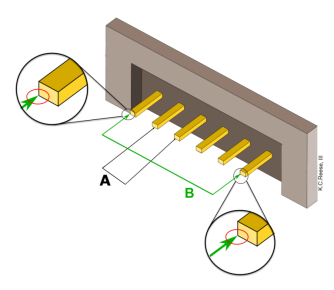
However, to measure the pitch of a connector, we typically measure from the center of one pin to the center of the next (A), as illustrated in Figure 2. Recognizing that this method can be challenging, there is an alternative approach. Here, you measure the distance from the outside edge of one pin to the inside edge of the last pin in the row (B). Make sure to count the number of pins in the row. The end results will be equivalent, as pitch A will be equal to pitch B.

Figure 3
The illustration above, Figure 3, depicts ribbon cables. To determine the pitch of a ribbon cable, utilize a similar procedure as that used to measure the connector’s pitch. This procedure will aid in understanding the distance between the cables. It is important to note that the connector pitch will differ from the ribbon cable’s pitch. In the case of a connector with two rows and a 2.54mm (0.1 inches) pin spacing, you will require a ribbon cable with a pitch that is half of the connector’s pitch for proper mating.
Conclusion
When dealing with connectors, it is crucial to know the pitch of each one. This is essential for ensuring compatibility with the wire or cable you intend to connect. Failing to do so may result in your cable not fitting the connector. If you wish to gain a deeper understanding of connector pitches, you can search for more information by typing queries such as “what is the ‘pitch’ of a connector?” or “What is pitch in a connector?” We will provide detailed responses to your questions and offer sufficient information.